More about Google Cloud Pricing
- Optimize Your Google Cloud Disk Storage Costs
- Google Cloud Pricing: The Complete Guide
- Understanding Google Cloud Storage Costs
- GCP Network Pricing: How to Beat the Hidden Fees
- Google Cloud Pricing vs AWS: A Fair Comparison?
- Google Cloud Storage Pricing: Get the Best Bang for Your Buckets
- Google Cloud Storage Efficiency: How to Reduce Storage Footprint and Costs with Cloud Volumes ONTAP
- Google Cloud SQL Pricing, and Limits: A Cheat Sheet for Cost Optimization
- Google Cloud Costs: Understanding and Managing Your GCP Bill
Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
March 1, 2021
Topics: Cloud Volumes ONTAP Cloud StorageStorage EfficienciesGoogle CloudElementary6 minute read
Google Cloud Storage is priced based on the data storage you consume, network usage and operations you perform on Google Cloud Storage objects, and special retrieval costs if you move data into Google’s low-cost cold storage tiers: Nearline, Coldline and Archive.
In this post, we’ll help you get the most of your storage buckets, by clarifying Google Cloud pricing, defining the service’s limits and usage conditions, and providing best practices for reducing your cost. In addition, we’ll show how NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP can help reduce storage costs on Google Cloud.
In this article, you will learn:
- Google Cloud Storage overview
- Data storage pricing
- Network usage, operations and retrieval pricing
- Google Cloud Storage quotas and limits
- Best Practices for Google Cloud Storage Price Optimization
- Reducing Google Cloud Storage costs with Cloud Volumes ONTAP
Google Cloud Storage Pricing Overview
Google Cloud Storage offers four storage classes with progressively lower storage costs, but higher retrieval costs: Standard (frequently used data), Nearline Storage (infrequently used data), Coldline Storage (rarely used data), and Archive Storage (long term archival).
Cloud Storage pricing is based on the following components:
- Data storage—quantity of data stored in Google Cloud Storage buckets
- Network usage—amount of data transferred to or from storage
- Operations use—actions performed on data within Google Cloud Storage
- Retrieval and early deletion fees—only applies to information saved in the three cold storage tiers (Nearline, Coldline, Archive).
Data Storage Pricing
Buckets are containers provided by Google Cloud Storage, which can be assigned to different storage classes. It is also possible to assign specific objects within a bucket to a different storage class. The storage price you pay in a given period depends on the storage class that was assigned to your bucket during that period.
Data storage pricing per storage class:
|
Storage Class |
Standard Storage |
Nearline Storage |
Coldline Storage |
Archive Storage |
|
Price / GB / Month |
$0.026 |
$0.010 |
$0.007 |
$0.004 |
Read our article on how to switch between storage classes in Google Storage Service, and how to define automated lifecycle rules for managing storage classes in Google Cloud Storage buckets.
Network Usage, Operations and Retrieval Pricing
Google Cloud Storage charges separately for networking usage, as follows:
- No charge for network egress
- No charge for network egress within the same location in Google Cloud
- $0.01/GB for egress between locations within the same continent
- $0.08-$0.12/GB for egress between continents (excluding Asia and Australia)
- $0.20-$0.23 for egress to China (excluding Hong Kong)
- $0.15-$0.19 for egress to Australia
In addition, there is a charge for data operations performed on data stored in Google Cloud Storage.
Charge for data operations per storage class:
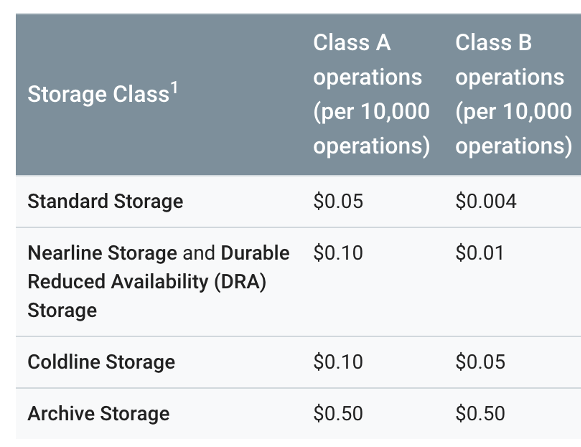 Source: Google Cloud
Source: Google Cloud
Notes:
- Class A refers to active data operations such as Insert, Update
- Class B refers to passive operations like Get
- Administrative actions on the data are provided for free
See a full list of data operations here.
Lastly, Google Cloud Storage charges for retrieval if you move data from the Standard storage class to one of the "colder" storage classes:
- $0.01/GB for retrieval from Nearline Storage
- $0.02/GB for retrieval from Coldline Storage
- $0.05/GB for retrieval from Archive Storage
Google Cloud Storage Quotas and Limits
Below we briefly explain the quotas and limits applicable to elements within the Google Cloud Storage solution.
Storage Buckets
- There is a per-project speed limitation to bucket creation and deletion. The limit may vary, but is usually one operation every two seconds. Plan on using fewer buckets with more objects per bucket.
- There is a limit for each bucket of one update per second, so quick updates to one bucket will not scale.
- You can have up to 100 users, groups, or domains with legacy IAM roles that can perform operations on one bucket. To understand the difference between standard, primitive, legacy and custom roles, see the official documentation.
Buckets with Pub/Sub notifications
- Up to 100 total notification configurations per bucket
- Up to 10 notification configurations set to trigger for a particular event per bucket
- Each notification configuration can have up to 10 custom attributes
Objects
- 5TB maximum size limit for each object stored in Cloud Storage
- 5TB Maximum size for one upload request
- Update limit of once per minute per object, so fast writes on a single object do not scale
- No limit to writes across multiple items—this includes reading a single object and uploading, updating, or deleting objects
- Publicly cacheable items provide better performance; you may use the item's Cache-Control metadata to serve fresh data
- Limit of 100 access control list entries (ACLs) for each object
- Composite objects have a 5TB size limitation
- Up to 32 objects may be written in a single object composition request
Best Practices for Google Cloud Storage Price Optimization
The following best practices can help you reduce costs and optimize your usage of Google Cloud Storage:
- Use lifecycle policies—lets you tag specific items or buckets and create an automatic rule that can delete objects, or change storage classes, reducing your ongoing storage costs for that data.
- Deleting objects after a minimum retention period—use lifecycle policies to detect that objects have met the minimum threshold of retention for legal compliance purposes, and then immediately delete it. This will make sure you don’t retain and pay for objects longer than actually needed. Cloud Storage provides a bucket lock attribute to minimize the chance for accidental deletion, to prevent issues with compliance standards like FINRA and SEC.
- Optimize your use of storage tiers—transforming objects automatically between storage classes is powerful, but should be used with care. Long-term storage is less expensive in terms of ongoing storage costs, but there are additional fees incurred if you need to access the data regularly. There are also minimum periods for data storage, so you may not be able to delete data if you realize it is not needed.
Reducing Google Cloud Storage Costs with Cloud Volumes ONTAP
NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP, the leading enterprise-grade storage management solution, delivers secure, proven storage management services on AWS, Azure and Google Cloud. Cloud Volumes ONTAP supports up to a capacity of 368TB, and supports various use cases such as file services, databases, DevOps or any other enterprise workload.
In particular, Cloud Volumes ONTAP provides storage efficiency features, including thin provisioning, data compression, and deduplication, reducing the storage footprint and costs on Google Cloud by up to 70%.
In addition, Cloud Volumes ONTAP provides data tiering, automatically and seamlessly moving infrequently-used data from block storage to lower-cost object storage and back as needed.
Visit Cloud Volumes ONTAP on Google Cloud TCO Calculator to see your expected savings.
Google Cloud Storage Pricing Q&A
What are Cloud Storage Always Free Usage Limits?
The Google Cloud Free Tier offers cloud-based storage resources that you can use for free, forever, until you reach a certain limit. You can use these resources during and after your free trial period.
For example, the Always Free tier can provide you with 5 GB-months of free standard storage, 5,000 class A operations, and 50,000 class B operations. However, if you exceed the Always Free limitations, expect to be charged according to the official pricing.
How Can You View Usage for a Cloud Storage Bucket?
There are two methods you can use to get a summary of space usage for your cloud storage bucket:
- Cloud Monitoring provides daily monitoring of the byte count of your bucket
- The gsutil du command can retrieve the total bytes in a bucket during a given time
What are Cloud Billing Reports?
Cloud Billing Reports provide information about your Google Cloud usage costs. The service comes with a dashboard that displays usage data at a glance. The Cloud Billing Reports provides a chart that shows storage usage costs for all projects associated with your Cloud Billing account.
You can view several metrics, which you can analyze to discover usage trends. For example, you can display a certain data range, define a time range, and configure a chart filter. You can also group by service, project, location, or SKU.
You can use Cloud Billing reports to understand several aspects, including:
- The Google Cloud spending trends of the current month
- Which Google Cloud project cost the most during last month
- In general, which Google Cloud service costs you the most
- Your forecasted future costs, calculated according to historical trends
- Total spendings by region

