More about Google Cloud Pricing
- Optimize Your Google Cloud Disk Storage Costs
- Google Cloud Pricing: The Complete Guide
- Understanding Google Cloud Storage Costs
- GCP Network Pricing: How to Beat the Hidden Fees
- Google Cloud Pricing vs AWS: A Fair Comparison?
- Google Cloud Storage Pricing: Get the Best Bang for Your Buckets
- Google Cloud Storage Efficiency: How to Reduce Storage Footprint and Costs with Cloud Volumes ONTAP
- Google Cloud SQL Pricing, and Limits: A Cheat Sheet for Cost Optimization
- Google Cloud Costs: Understanding and Managing Your GCP Bill
Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
October 4, 2021
Topics: Cloud Volumes ONTAP Storage EfficienciesGoogle CloudElementary9 minute read
How Do You Determine Google Cloud Storage Cost?
Google Cloud Storage is designed to group objects into buckets. A bucket is a cloud-based container that can be assigned one of several storage tiers. Individual objects can also be assigned to a specific storage tier. Google Cloud Storage provides four tiers, and each offers different pricing and retrieval costs.
The main storage tiers in Google Cloud Storage are Standard Storage, Nearline Storage (for frequently accessed data), Coldline Storage (for cold data accessed once per year), and Archive Storage (for long-term archiving with the minimum duration starting at 365 days).
Google Cloud pricing for storage is affected by additional components, including network usage and operations carried out within the storage service. Retrieval and early deletion of data is also subject to fees in the three archival tiers (but not in the Standard Storage tier).
In this article:
- Google Cloud Storage Tiers
- Google Cloud Storage Cost Components
- Optimizing Google Cloud Storage Costs with Cloud Volumes ONTAP
Google Cloud Storage Tiers
Google Cloud Storage costs are largely determined by the storage tier you select for your data. Here are the tiers offered by Google Cloud Storage, from Standard Storage with the highest cost per GB-hour, to Archive Storage which has the lowest cost.
Standard Storage
Standard Storage is suitable for frequently accessed data (“hot” data) and/or kept only for limited time periods.
When using Standard Storage in a single region, it is best to store data used by Compute Engine instances or Google Kubernetes Engine clusters running within the same region. Co-locating your resources optimizes the performance for in-depth data computations and could minimize network charges.
When employed in dual- or multi-region mode, you still receive maximum performance when using Google Cloud products, which are found in one of the related regions, yet you also receive the better availability derived from storing information in geographically distinct locations.
Standard Storage costs:
- $0.026 per GB-month for storage
- No cost for data retrieval
Nearline Storage
Nearline Storage is a low-budget, durable storage solution for retaining data that is not often accessed. Nearline Storage is a preferred choice over Standard Storage in situations where a 30-day minimum storage timeframe, slightly less availability, and charges for data access are admissible trade-offs for lower at-rest storage bills.
Nearline storage is suitable for data you wish to modify or read on an average of one time per month or less. For instance, if you wish to add more files to Cloud Storage on a continual basis, and plan on accessing those files one time per month for examination, Nearline Storage is a good option.
Nearline Storage costs:
- $0.010 per GB-month for storage
- $0.01/GB for data retrieval
Coldline Storage
Coldline Storage is a highly durable, low-cost service for storing data which is infrequently accessed. Coldline Storage is a superior option than Nearline Storage or Standard Storage in situations where a 90-day minimum storage time, a tiny bit less availability, and higher costs related to data access are admissible trade-offs for less at-rest storage charges.
Nearline Storage costs:
- $0.007 per GB-month for storage
- $0.02/GB for data retrieval
Archive Storage
Archive Storage is Google’s lowest-cost storage service for data archiving disaster recovery and online backup. As opposed to the “coldest” storage solution provided by other Cloud suppliers, your data is accessible within milliseconds, rather than hours or days.
Similar to Coldline Storage and Nearline Storage, Archive Storage has moderately lower accessibility than Standard Storage. In addition, archive Storage has greater costs for information operations and access, and a 365-day minimum storage length. Archive Storage is suitable for data that you plan to retrieve less than one time per year.
Related content: read our blog post Making the Most of Google’s Storage Tiers for Backup
Nearline Storage costs:
- $0.004 per GB-month for storage
- $0.05/GB for data retrieval
The cost of data storage for each of the four data tiers is summarized in the following table.
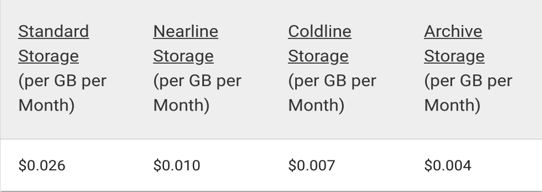 Source: Google Cloud
Source: Google Cloud
Related content: read our blog post How to Add and Manage Lifecycle Rules in Google Cloud Storage Buckets
Additional classes
Cloud Storage supports some additional, legacy storage classes. These classes cannot be accessed via the Cloud Console. Unless you are already using one of these classes, Google recommends using Standard Storage.
- Multi-regional storage—comparable to Standard Storage, exculting multi-regional storage may only be employed for objects stored in dual-regions or multi-regions
- Regional storage—comparable to Standard Storage, excluding Regional Storage may only be employed for objects retained in regions
- Durable reduced Availability (DRA) storage—like Standard Storage, except DRA incurs greater prices for operations. Also, DRA has lower performance, specifically in relation to availability (DRA has a 99% availability SLA)
Google Cloud Storage Cost Components
Google Cloud Storage bills you according to the amount of data storage used, data transferred to and from cloud storage, data operations, and data retrieval (for archival tiers).
Data storage
Data storage charges are computed according to sub-seconds for every object, and data storage rates are calculated according to the storage tier of every object, not the default storage tier assigned to the bucket that holds them.
Note that Coldline Storage, Archive Storage, and Nearline Storage data incurs additional charges if you change or delete it more frequently than allowed by the tier specifications.
As well as the data contained within your uploaded objects, these factors contribute to monthly storage usage:
- Custom metadata—for instance, for the custom metadata NAME:VALUE, Cloud Storage calculates every character in VALUE and NAME as a byte stored alongside the object.
- XML API multipart—if you perform a multipart upload, you are billed for the uploaded parts, up to the point where the multipart upload is stopped or completed.
Network
Egress is data transferred from Cloud Storage in HTTP responses. Metadata or data read from a Cloud Storage bucket is a type of egress.
Ingress is data transferred from Cloud Storage in HTTP requests. Metadata or data written to a Cloud Storage bucket is a type of ingress.
Network usage billing apply for egress and can be categorized into the cases as follows:
- Network egress within the same Google Cloud region—when egress is to Google Cloud services or to other Cloud Storage buckets in the same region, there is no charge.
- Network egress between locations in the same continent—charged at $0.01/GB.
- Network egress between continents (except Asia and Australia)—charged at $0.08-$0.012
- Network egress to China—charged at $0.20-$0.23
- Network egress to Australia—charged at $0.15-$0.19
Related content: read our blog post Hidden Google Cloud Network Transfer Costs and How to Avoid Them
Operations
Operation costs apply when you carry out operations within Cloud Storage. An operation is an activity that makes modifications to or gains access to details about resources, including objects and buckets in Cloud Storage.
Operations can be placed into one of three categories: free, Class A, and Class B. The storage class of an operation is decided according to the following factors:
- When listing buckets in a task, the Class A rate will always apply
- When an operation concerns a bucket, for example listing the objects within a bucket, the default storage class established for the bucket will influence the operation cost
- When an operation concerns an object, the storage class of a given object influences the operation cost
- When modifying the storage class of a given object, through manual means or with Object Lifecycle Management, a Class A rate connected to the object’s destination storage class is relevant. For instance, modifying 1,000 objects from Standard Storage to Coldline Storage adds up to 1,000 Class A operations at the Coldline Storage rate
This table summarizes data operation costs for each class:
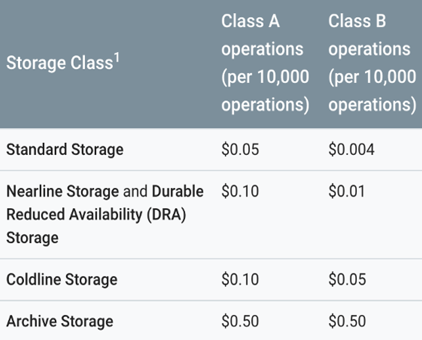 Source: Google Cloud
Source: Google Cloud
Retrieval and Early Deletion
Coldline Storage, Nearline Storage, and Archive Storage are meant for storing data that is not regularly accessed. Therefore, there are more costs connected to retrieving metadata or data stored in these classes, and you are also charged for minimum storage durations.
- A retrieval cost comes into effect when you copy, read, or rewrite metadata or data that is retained using any of these classes. The cost is on top of any network charges connected to reading the data
- A minimum data storage duration is incurred when data is retained using any of these storage classes. You could delete the information before it was stored for this period of time, but at the moment of deletion you will be billed as if the data was retained for the minimum period of time
- In buckets that employ Object Versioning, these charges of early deletion are relevant when an object version is taken out of the bucket, and not when it is no longer current. Early deletion costs are charged via early delete SKUs
- For XML API multipart uploads, a section may incur early deletion costs if it is not utilized when assembling the end object, or if the section is overwritten by a different section, or when the multipart upload is stopped
- The storage duration of every section in a multipart upload starts at the point the upload of the section finishes, and the storage time for an overall object starts when an object is constructed
This table summarizes data retrieval costs for the different tiers:
|
Data Tier |
Retrieval Cost/GB |
|
Standard Storage |
No cost |
|
Nearline Storage |
$0.01 |
|
Coldline Storage |
$0.02 |
|
Archive Storage |
$0.05 |
Optimizing Google Cloud Storage Cost with Cloud Volumes ONTAP
NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP, the leading enterprise-grade storage management solution, delivers secure, proven storage management services on AWS, Azure and Google Cloud. Cloud Volumes ONTAP capacity can scale into the petabytes, and it supports various use cases such as file services, databases, DevOps or any other enterprise workload, with a strong set of features including high availability, data protection, storage efficiencies, Kubernetes integration, and more.
In particular, Cloud Volumes ONTAP provides storage efficiency features, including thin provisioning, data compression and deduplication, and data tiering, reducing the storage footprint and costs by up to 70%.
Learn more about how Cloud Volumes ONTAP helps cost savings with these Cloud Volumes ONTAP Storage Efficiency Case Studies.

