Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
February 8, 2023
Topics: Cloud Volumes ONTAPAstra Advanced15 minute readKubernetesKubernetes Protection
Now it’s easier than ever to manage Kubernetes (K8s) clusters on Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud. With its latest January update, NetApp® Astra™ Control Service also supports NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP® software as a storage back end for your protected K8s clusters on Azure and Google Cloud platforms.
Cloud Volumes ONTAP is a software-only storage appliance that runs NetApp ONTAP data management software in the cloud. You get enterprise-grade storage features and extended support in Astra Control Service to:
- NetApp Cloud Volumes Service for Google Cloud, Google Persistent Disk, and NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP as the storage back ends for Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters
- Azure NetApp Files, Azure Managed Disks, and NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP as the storage back ends for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) clusters
- Amazon Elastic Block Store and Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP as the storage back ends for Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) clusters
In this blog post, I show you how to configure Cloud Volumes ONTAP as a storage back end for an example AKS cluster (pu-aks-cvo-01). I also show you how to manage and to protect the AKS cluster with Astra Control Service.
Steps to configure Cloud Volumes ONTAP as a back end
To make it easy to manage Cloud Volumes ONTAP and configure it as a storage back end for the AKS cluster, we use the NetApp BlueXP™ unified control plane in this setup. With BlueXP, you can manage all your storage and data assets from a single intuitive web-based interface.
Keep in mind that although this walk-through uses Cloud Volumes ONTAP for Azure and AKS clusters, you use a similar process for setting up Cloud Volumes ONTAP for Google Cloud and GKE clusters.
First, log in to the BlueXP management console (see how to set up BlueXP), then select the correct account, workspace, and connector to your Azure environment. Now you can manage an already existing Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance, which is acsakscvobackend in this example, in Storage -> Canvas -> My Working Environments:
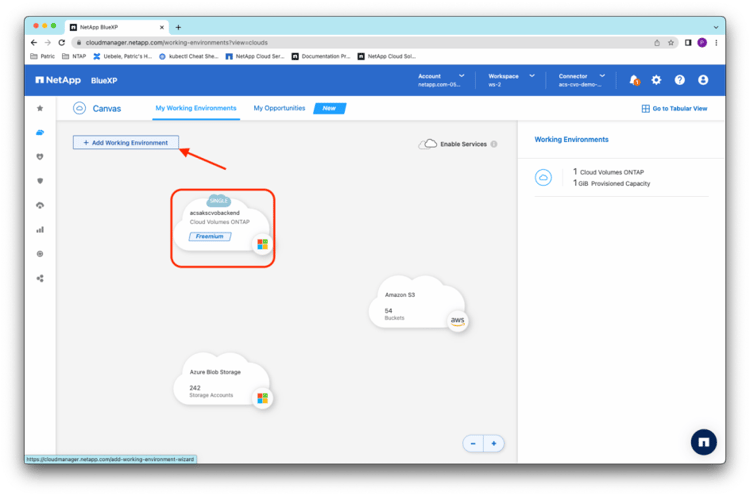 By clicking the + (Add Working Environment) button in the Canvas, you’re guided through the dialog box to add resources and to select Microsoft Azure as the platform and Kubernetes Cluster as the resource type. After your selection, click Next:
By clicking the + (Add Working Environment) button in the Canvas, you’re guided through the dialog box to add resources and to select Microsoft Azure as the platform and Kubernetes Cluster as the resource type. After your selection, click Next:
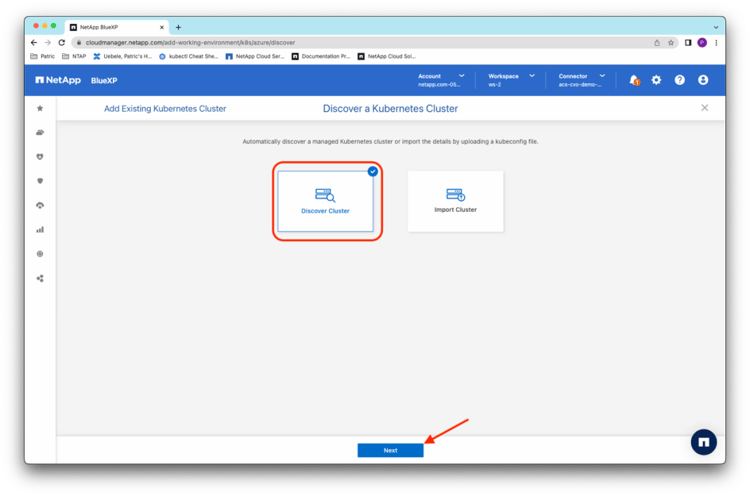
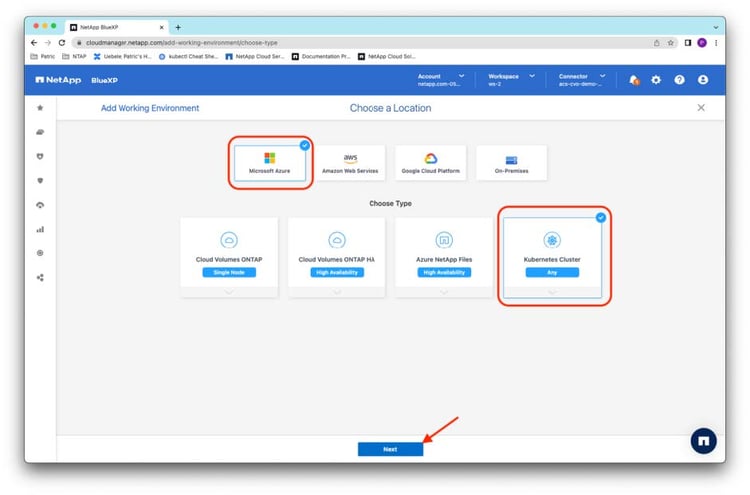 Then select Discover Cluster to discover existing AKS clusters through the BlueXP Connector and click Next:
Then select Discover Cluster to discover existing AKS clusters through the BlueXP Connector and click Next:
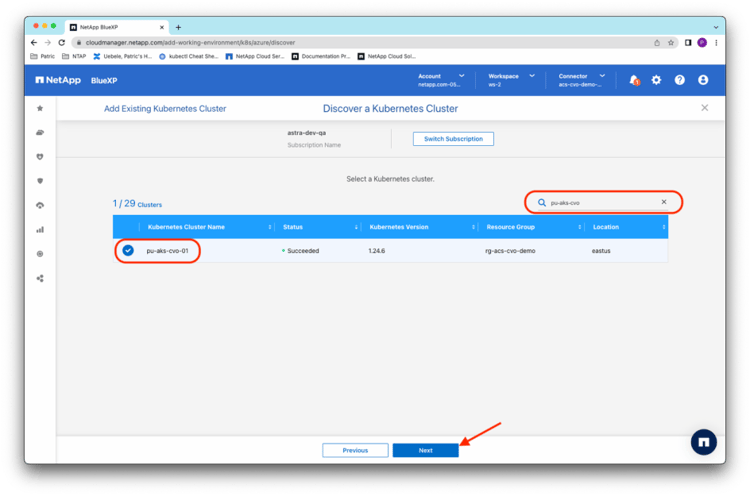
 Search for the test cluster pu-aks-cvo-01 in the list of discovered clusters, and click Next to add it to BlueXP:
Search for the test cluster pu-aks-cvo-01 in the list of discovered clusters, and click Next to add it to BlueXP:
 The AKS cluster now appears among the working environments in the BlueXP Canvas, with a request for further configuration:
The AKS cluster now appears among the working environments in the BlueXP Canvas, with a request for further configuration:
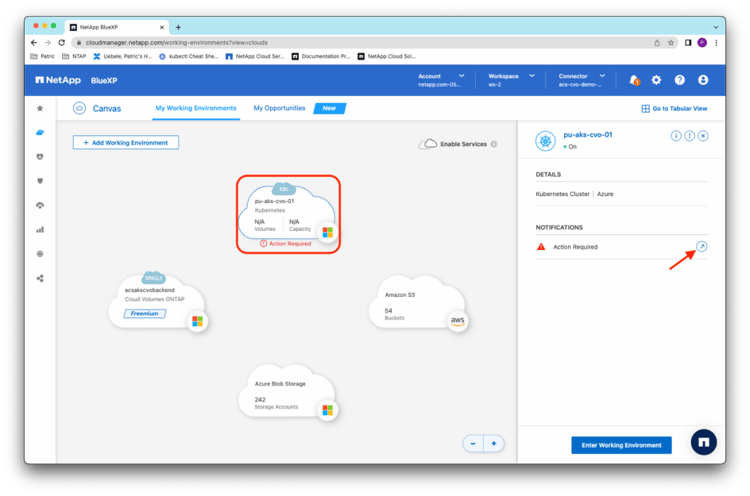 After you enter the working environment, click Install Trident to let BlueXP configure NetApp Astra Trident, a storage provisioner and orchestrator for the entire NetApp storage portfolio, on the AKS cluster:
After you enter the working environment, click Install Trident to let BlueXP configure NetApp Astra Trident, a storage provisioner and orchestrator for the entire NetApp storage portfolio, on the AKS cluster:
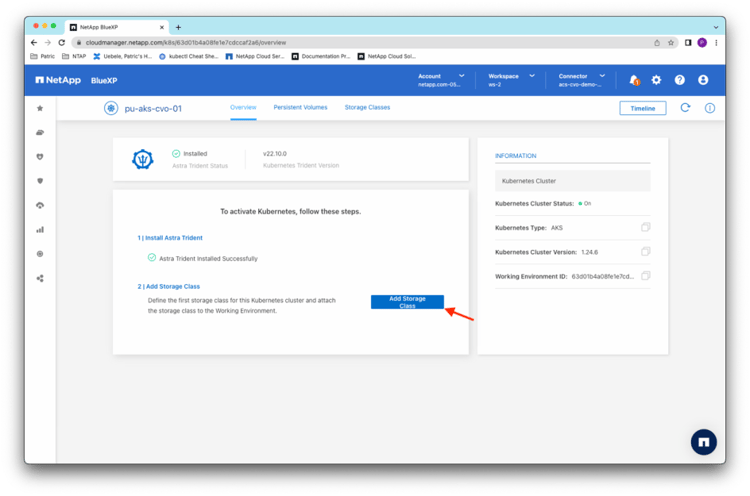 Trident installation takes a moment. After the installation is complete, you receive a message, at which point you can proceed with adding a storage class for the cluster. Click Add Storage Class:
Trident installation takes a moment. After the installation is complete, you receive a message, at which point you can proceed with adding a storage class for the cluster. Click Add Storage Class:

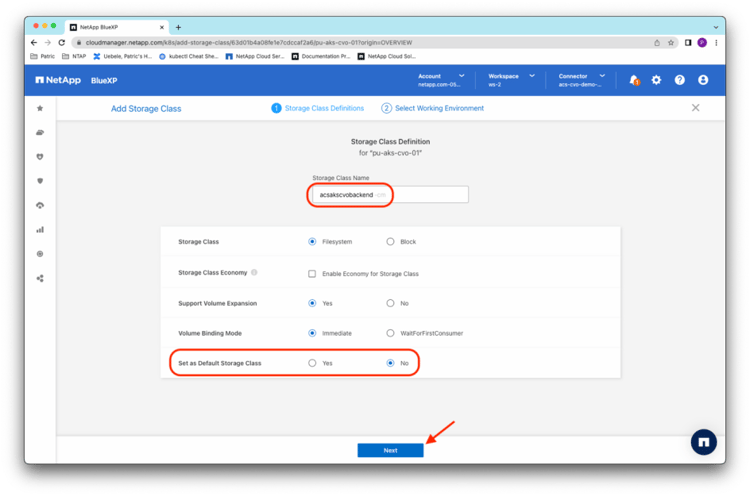
Provide a storage class name and the configuration details for the storage class. Select No in Set as Default Storage Class, because Astra Control Service does that step later. Click Next:
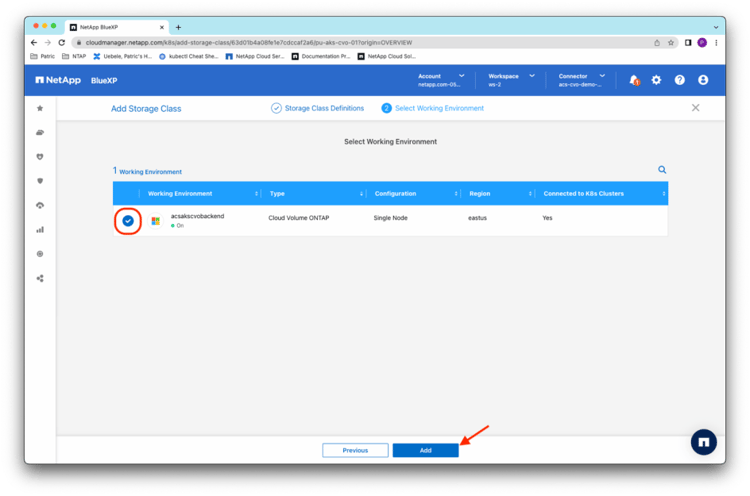
BlueXP searches for available Cloud Volumes ONTAP instances to be configured as a K8s persistent storage back end. In this example, you select the Cloud Volumes ONTAP system acsakscvobackend and click Add to create the storage class and to configure Cloud Volumes ONTAP as its storage back end:
 After a few seconds, you’re taken to the configuration overview of the cluster in BlueXP:
After a few seconds, you’re taken to the configuration overview of the cluster in BlueXP:
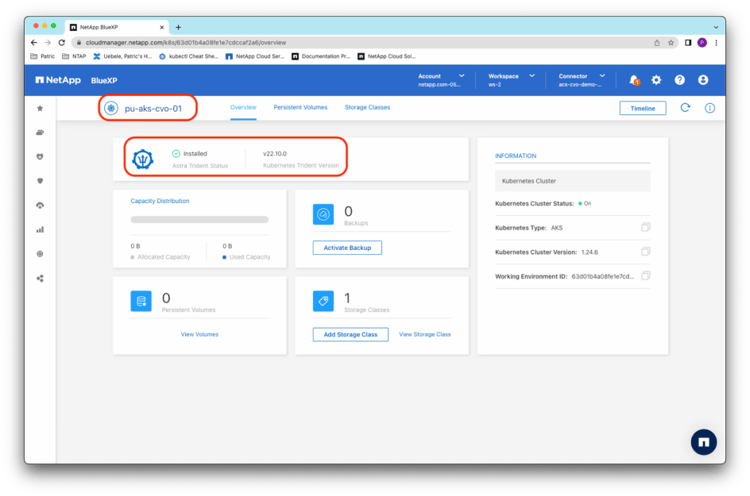 Back in the BlueXP storage Canvas, you now see that the AKS cluster pu-aks-cvo-01 is connected to the Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance acsakscvobackend:
Back in the BlueXP storage Canvas, you now see that the AKS cluster pu-aks-cvo-01 is connected to the Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance acsakscvobackend:
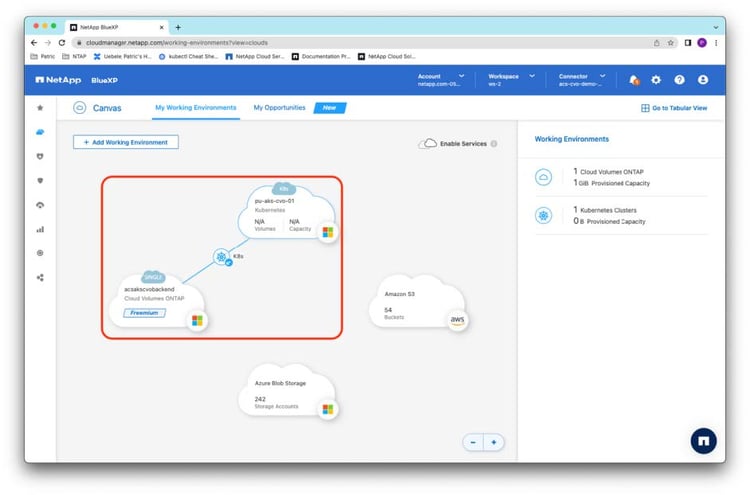 The connection between your Cloud Volumes ONTAP storage back end and Kubernetes cluster has now been set up and verified.
The connection between your Cloud Volumes ONTAP storage back end and Kubernetes cluster has now been set up and verified.
Steps to set up management and protection in Astra Control Service
Now you’re all set to manage and to protect your AKS cluster with Astra Control Service. You can also deploy applications with persistent volumes that are backed by Cloud Volumes ONTAP on the cluster.
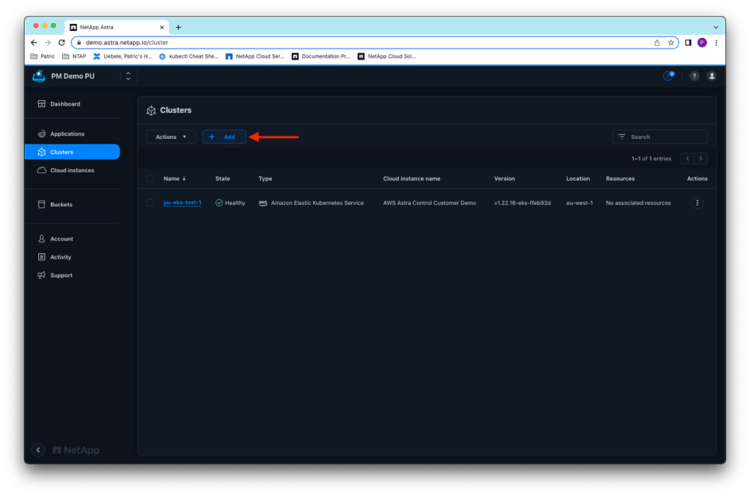
Switch to the Astra Control Service console, and add the AKS cluster pu-aks-cvo-01 to Astra Control Service:
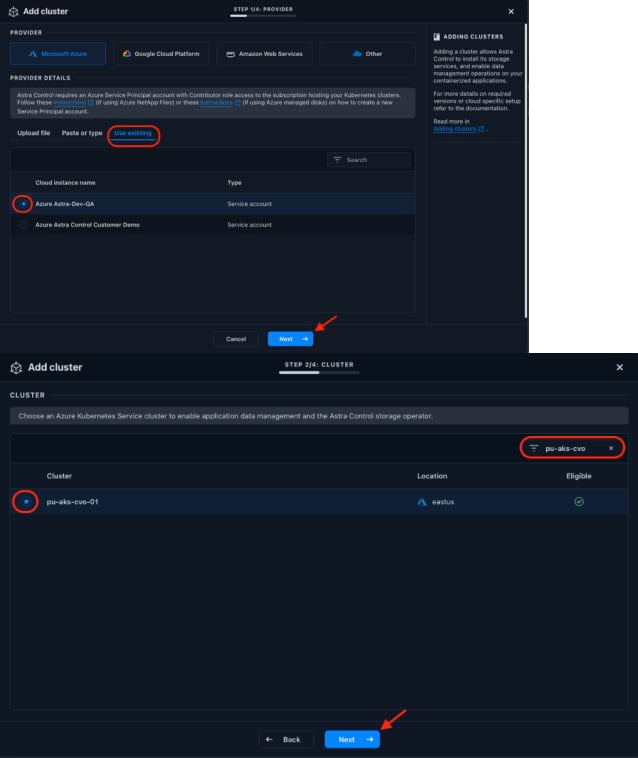
 The already configured Service Principal allows Astra Control Service to discover the available clusters in the Azure subscription, and you can filter for the pu-aks-cvo-01 cluster name. After you select the cluster, click Next:
The already configured Service Principal allows Astra Control Service to discover the available clusters in the Azure subscription, and you can filter for the pu-aks-cvo-01 cluster name. After you select the cluster, click Next:
During the process of adding the cluster to Astra Control Service, you’re asked whether you want to assign a new default storage class. Select as the new default storage class the Cloud Volumes ONTAP backed acsakscvobackend-cm storage class that was configured by BlueXP in the previous steps. When you have finished, click Add:
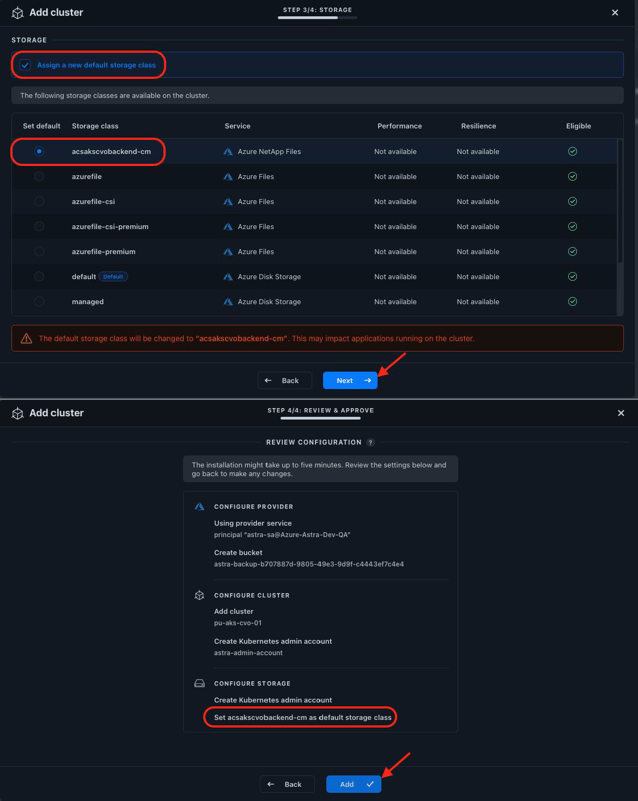
Astra Control Service detects that Astra Trident is already installed and configured on the AKS cluster and changes the default storage class to acsakscvobackend-cm:
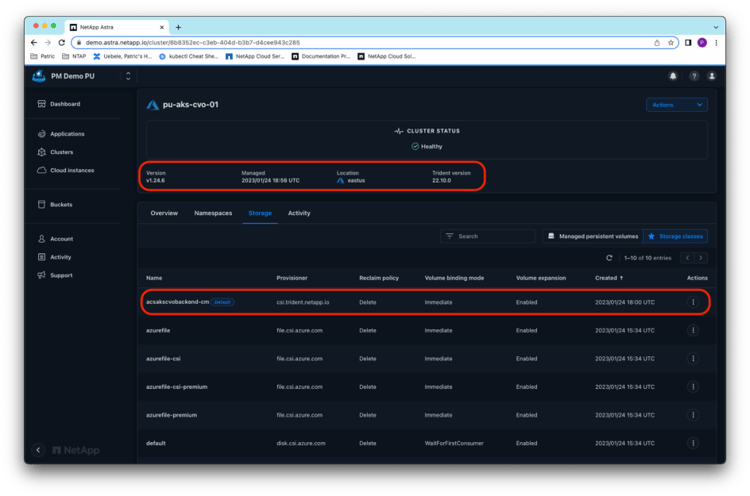 Now you’re ready to protect persistent applications on the AKS cluster with NetApp Snapshot™ copies and backups from Astra Control Service. As a demonstration application, here a WordPress instance is quickly deployed through its Bitnami Helm chart in the namespace wordpress:
Now you’re ready to protect persistent applications on the AKS cluster with NetApp Snapshot™ copies and backups from Astra Control Service. As a demonstration application, here a WordPress instance is quickly deployed through its Bitnami Helm chart in the namespace wordpress:
~# helm install wordpress bitnami/wordpress --namespace wordpress --set wordpressUsername=astra,wordpressPassword=XXXXXXX --create-namespaceBecause acsakscvobackend-cm is set as the default storage class, the two persistent volumes for WordPress are backed by the Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance:
NAME: wordpress
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Jan 24 19:00:53 2023
NAMESPACE: wordpress
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: wordpress
CHART VERSION: 15.2.19
APP VERSION: 6.1.1
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
Your WordPress site can be accessed through the following DNS name from within your cluster:
wordpress.wordpress.svc.cluster.local (port 80)
To access your WordPress site from outside the cluster follow the steps below:
1. Get the WordPress URL by running these commands:
NOTE: It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
Watch the status with: 'kubectl get svc --namespace wordpress -w wordpress'
export SERVICE_IP=$(kubectl get svc --namespace wordpress wordpress --include "")
echo "WordPress URL: http://$SERVICE_IP/"
echo "WordPress Admin URL: http://$SERVICE_IP/admin"
2. Open a browser and access WordPress using the obtained URL.
3. Login with the following credentials below to see your blog:
echo Username: astra
echo Password: $(kubectl get secret --namespace wordpress wordpress -o jsonpath="{.data.wordpress-password}" | base64 -d)
~# kubectl get all,pvc -n wordpress
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/wordpress-57bd45f7b-8zbr2 1/1 Running 1 (3m25s ago) 4m56s
pod/wordpress-mariadb-0 1/1 Running 0 4m56s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/wordpress LoadBalancer 10.4.62.227 20.75.179.28 80:32481/TCP,443:31567/TCP 4m57s
service/wordpress-mariadb ClusterIP 10.4.126.147 <none> 3306/TCP 4m57s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/wordpress 1/1 1 1 4m57s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/wordpress-57bd45f7b 1 1 1 4m57s
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/wordpress-mariadb 1/1 4m57s
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/data-wordpress-mariadb-0 Bound pvc-2936728e-1f87-4b7f-9490-2ba1b5009690 8Gi RWO acsakscvobackend-cm 4m58s
persistentvolumeclaim/wordpress Bound pvc-96ad0163-ec69-4cb1-9ec6-eeea2f2a7c56 10Gi RWO acsakscvobackend-cm 4m58s
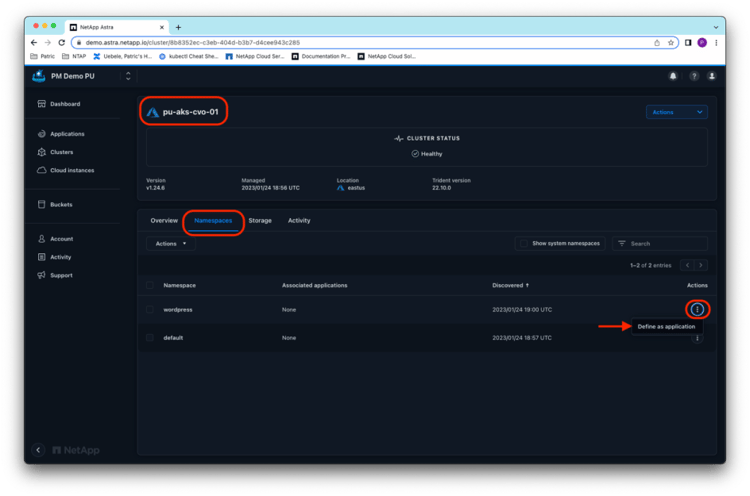
Astra Control Service automatically detects the newly created namespace for WordPress on cluster pu-aks-cvo-01, and you can easily define the whole wordpress namespace as an application in Astra Control Service. When you have finished, click View in Applications:
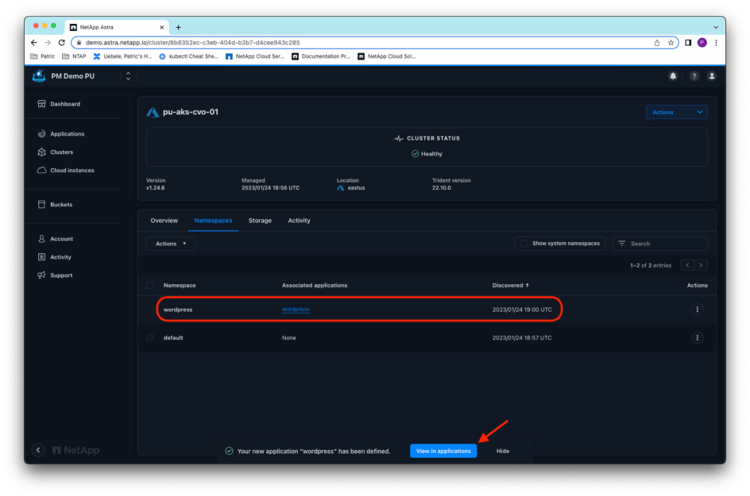 From the WordPress application details in the Astra Control Service application view, you can directly create the first Snapshot copy of the application:
From the WordPress application details in the Astra Control Service application view, you can directly create the first Snapshot copy of the application:
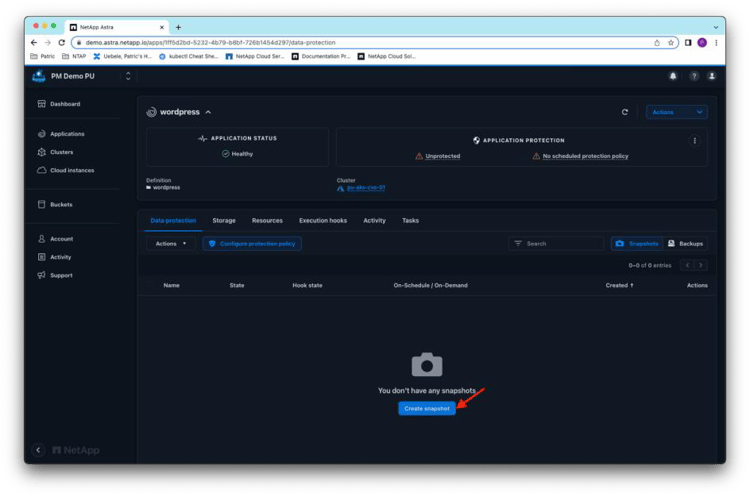
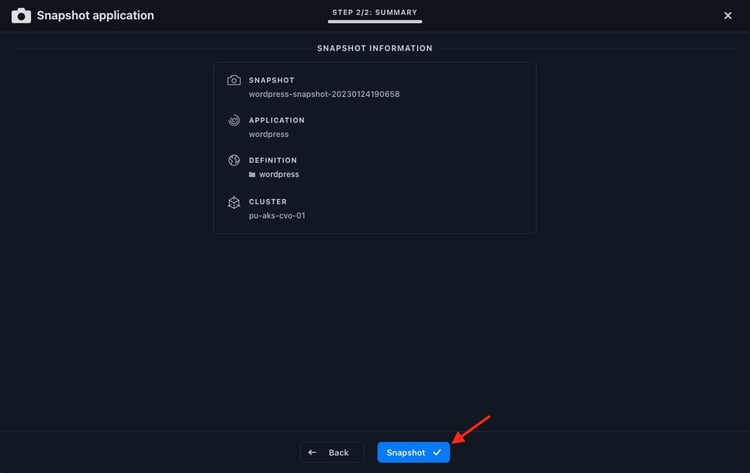
The Snapshot copies take only a few seconds to be created, because they’re created by using the fast and efficient ONTAP Snapshot mechanisms:
~# kubectl get pvc,volumesnapshots -n wordpress
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/data-wordpress-mariadb-0 Bound pvc-2936728e-1f87-4b7f-9490-2ba1b5009690 8Gi RWO acsakscvobackend-cm 7m
persistentvolumeclaim/wordpress Bound pvc-96ad0163-ec69-4cb1-9ec6-eeea2f2a7c56 10Gi RWO acsakscvobackend-cm 7m
NAME READYTOUSE SOURCEPVC SOURCESNAPSHOTCONTENT RESTORESIZE SNAPSHOTCLASS SNAPSHOTCONTENT CREATIONTIME AGE
volumesnapshot.snapshot.storage.k8s.io/pvc-2936728e-1f87-4b7f-9490-2ba1b5009690-snap-c83ed35b-15d2-4a56-8637-dc20f59f7c53 true data-wordpress-mariadb-0 33676Ki astra-netapp-csi-trident-netapp-io-vsc snapcontent-6fcb2070-5c1d-4a23-80e1-321dd46c2e3d 36s 37s
volumesnapshot.snapshot.storage.k8s.io/pvc-96ad0163-ec69-4cb1-9ec6-eeea2f2a7c56-snap-c83ed35b-15d2-4a56-8637-dc20f59f7c53 true wordpress 250100Ki astra-netapp-csi-trident-netapp-io-vsc snapcontent-7b2a73da-f151-44b9-96c3-cd47f030e18d 36s 36s
Finally, with the application Snapshot copy in place, you can test a restore of the application to a new namespace on the same cluster. From the Actions menu of the Snapshot copy in Astra Control Service, you can directly start a restore by clicking Restore Application:
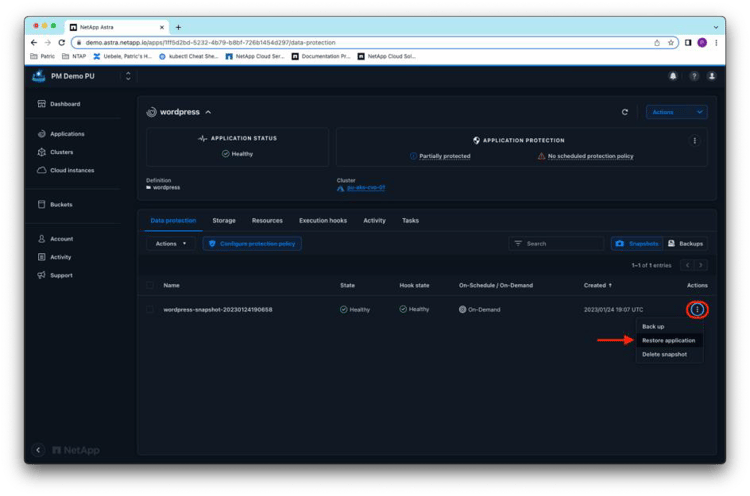 Select wordpress-clone as the destination namespace and click Next:
Select wordpress-clone as the destination namespace and click Next:
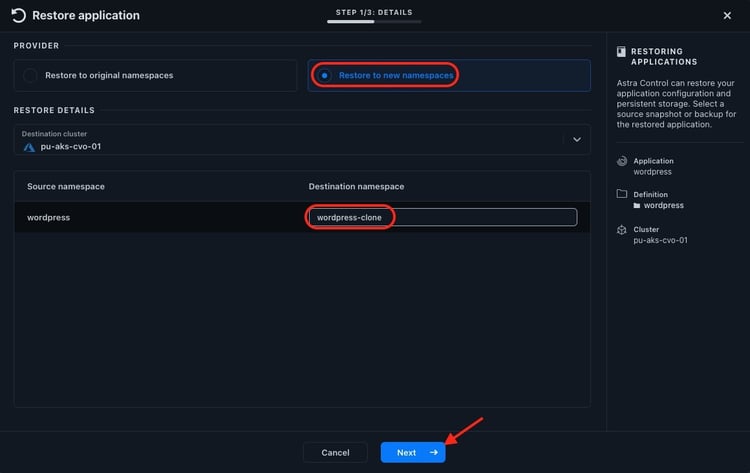
Then start the restore after you check the restore information:
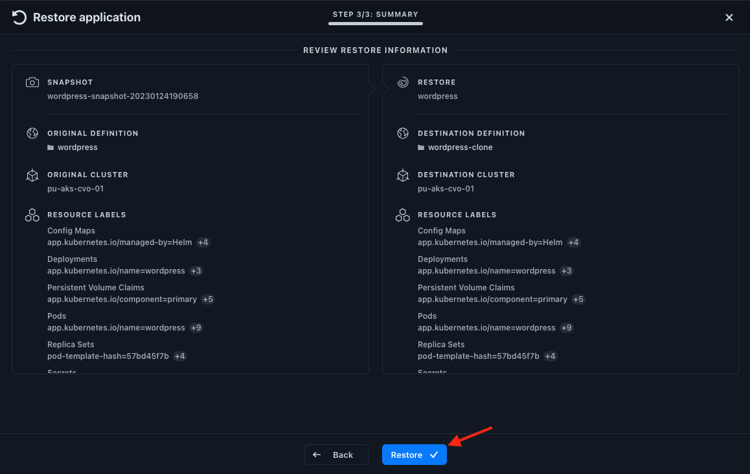
After a short while, the restored WordPress application in the new namespace comes up. Then you can confirm that its two persistent volumes also exist in the acsakscvobackend-cm storage class and are backed by Cloud Volumes ONTAP:
~# kubectl get all,pvc -n wordpress-clone
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/wordpress-65bccc5b66-d9jrz 1/1 Running 0 2m22s
pod/wordpress-mariadb-0 1/1 Running 0 2m22s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/wordpress LoadBalancer 10.4.8.187 20.62.183.37 80:30065/TCP,443:31078/TCP 2m22s
service/wordpress-mariadb ClusterIP 10.4.154.28 <none> 3306/TCP 2m22s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/wordpress 1/1 1 1 2m23s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/wordpress-65bccc5b66 1 1 1 2m23s
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/wordpress-mariadb 1/1 2m23s
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/data-wordpress-mariadb-0 Bound pvc-39d96f88-a1b1-4054-a716-f2dba111e996 8Gi RWO acsakscvobackend-cm 2m25s
persistentvolumeclaim/wordpress Bound pvc-39b4c713-ecb9-4cf7-88b2-78c05a279c5f 10Gi RWO acsakscvobackend-cm 2m25s
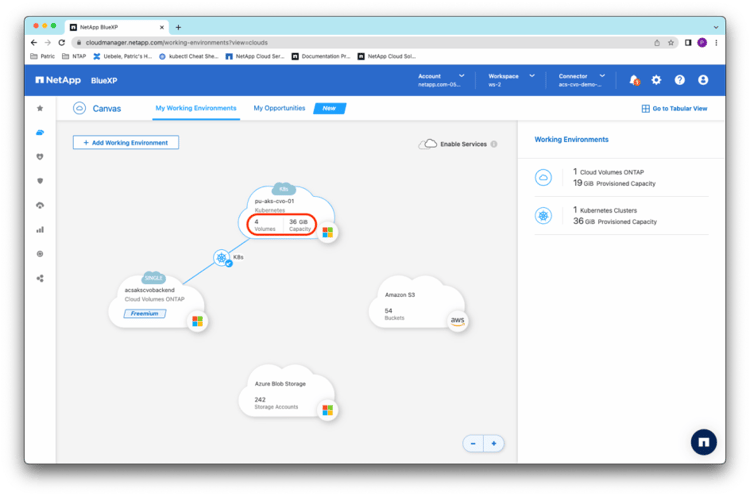
Checking back in the BlueXP storage Canvas, you see that BlueXP detected the four created persistent volumes on the AKS cluster:
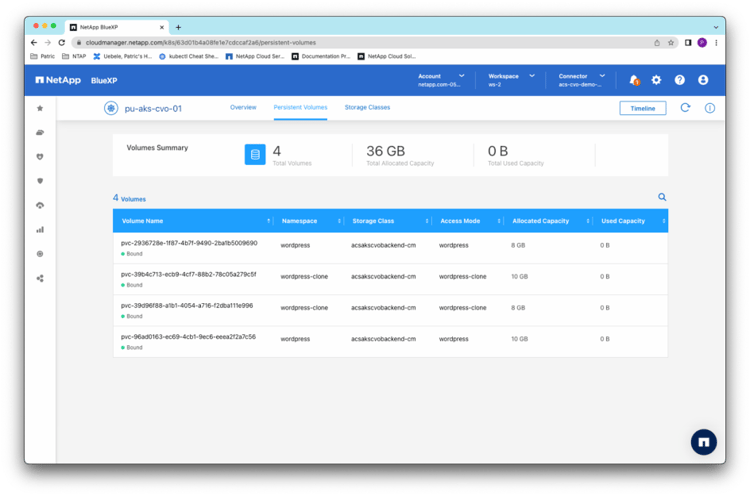
You can also find more details about the persistent volumes by drilling down into the pu-aks-cvo-01 AKS cluster:
Take advantage of NetApp’s continued innovation
With expanded Cloud Volumes ONTAP support for NetApp Kubernetes users, now you have yet another choice to store your persistent application data in GKE and AKS clusters.
Because NetApp continually innovates and enhances its product capabilities, now Astra Control Service can seamlessly manage and protect Cloud Volumes ONTAP backed persistent applications. In this blog post, I showed how easy it is to deploy Cloud Volumes ONTAP as a storage back end in Astra Control Service, so why wait? Get started today