Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
February 9, 2023
Topics: Cloud Data Sense Data MigrationAdvanced7 minute readData Governance
Migrating data at the enterprise level is a challenging undertaking that requires careful planning. The key to such plans, and making those migrations work, is knowing your data.
But what if you’re missing that crucial insight into your data?
As we’ll see below, a lack of visibility and knowledge of an organization's data can seriously jeopardize—and sometimes even ruin—a migration project. In our follow-up blog, we’ll look at six steps to preventing migration failures. For complete coverage on this topic, download our full ebook: Why Data Migration Projects Fail (and What You Can Do About It).
Use the links below to jump down to the sections on:
- What Makes Migration So Important?
- The Difficult Path to Successful Migration
- Why Do Data Migrations Fail?
- Data Migration Done Right
- FAQ
What Makes Migration So Important?
Data fuels organizations, so where that data resides determines how effectively those organizations can run. If there is a better place for the data to be located, it should be there. Data migrations are how that happens.
While data migration today is most frequently associated with adopting the cloud, or between clouds, data also needs to be moved between on-premises repositories, whether for hardware updates or consolidation efforts, and as part of comprehensive hybrid cloud architectures.
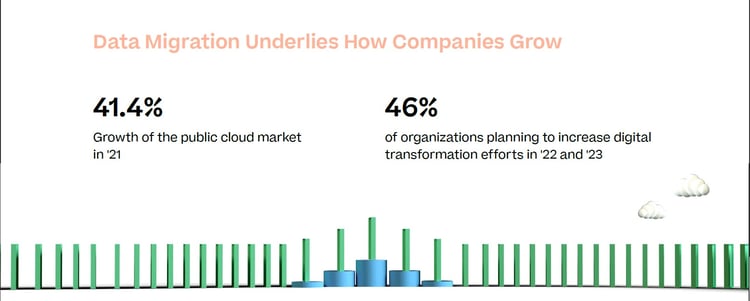
But since the majority of data migrations involve the cloud, it’s important to understand just how much these migrations play into the growth plans for organizations. Gartner recently reported the public cloud market has ballooned, growing 41.4% in 2021, and that cloud spending is projected to grow 20.7% in 2023, coming to a $591.8 billion total. The report adds that even if IT budgets need to shrink in the face of recent financial changes, the cloud makes such scalability possible—but you need to get there first. For organizations that are transitioning to a new cloud platform from an on-prem data center or from one cloud provider to another, the migration process is key to succeeding in the new environment.
Another factor to consider is how the cloud factors into growth. To meet the demands of current business trends, 46% of organizations are planning to scale up by increasing digital transformation efforts 2022 and 2023. As new platforms are adopted, data migration will be a key part to enabling those investments.
However, getting to the cloud is not as easy as it sounds.
The Difficult Path to Successful Migration

For enterprises, the prospect of a data migration can be a daunting one. It requires intense levels of planning, investment, and governance. The process will affect every aspect of IT operations, all while trying to remain non-disruptive to normal operations, under budget, and on schedule. These challenges can be so difficult that many migration projects fail.
When migration plans fail, it doesn’t just make the migration itself difficult. Problems at the planning stage persist: research shows that poor planning can lead to failure in the new environment. In some cases only 16% finished on time and under budget and more than 80% of migrations either fail to deliver on time and/or go over budget.
How bad can these problems get? One mismanaged data migration led to the loss of more than 24 TB of highly sensitive data. For industries that are highly regulated, the migration can pose a risk that can lead to major fines and further financial consequences.
Why Do Data Migrations Fail?
There are a number of contributing factors to migration failures. Just as every migration is unique because every organization’s data set and architecture is different, so are the reasons behind the failures.
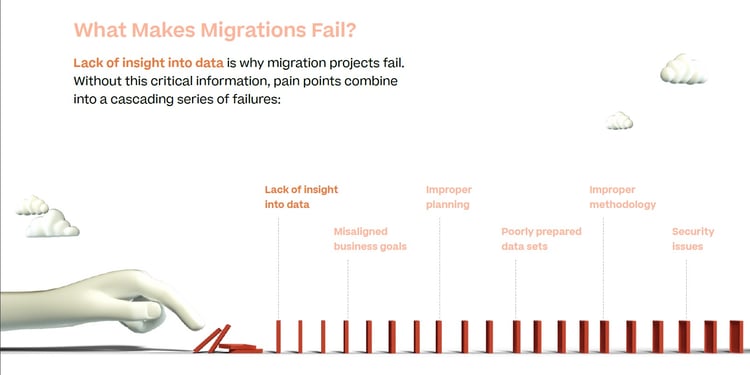
However, there is some common ground that all migration failures share. And the reason behind that commonality is that all of these failures are due to one primary factor: lack of insight into data.
- Lack of insight into data is at the heart of migration failure. Without critical insights into the data set that needs to be migrated, a number of different pain points occur, leading to a cascading series of failures.
Gaining this level of visibility requires a high level of data governance. That can be a major challenge in enterprise-scale deployments, where data is likely scattered across many silos, and in some across multiple global regions.
Without this level of data governance, it can be impossible to answer where the data that needs to be migrated is located, how much is necessary to move to the cloud, which users will be affected, how much time the migration will take, and how to keep the data secure.
From this single misalignment, your migration is likely to face the other migration failure points covered in this list.- Misaligned business goals
- Improper project scoping
- Poorly prepared data sets
- Improper migration methodology
- Security issues
- Misaligned business goals
When migrations don’t take stock of the data to be migrated, it’s impossible to know which business elements will be affected or for stakeholders to make proper preparations.
Without insight into your business goals, your migration can:- Disrupt business when teams aren’t aware of the changes
- Lead to regulatory violations if data is moved improperly
- Slow down operations when onboarding new applications post-migration
- Improper project scoping
Scoping is essential to successful migration, but as many failed migrations show, such planning is often neglected. There are reasons why this might make sense in the short term, but it leads to long-term problems.
Poor scoping can lead to:- Overshooting project budget
- Missing migration deadlines
- Migrating problem data that can create issues in the new environment
- Miscommunication between team members
- Poorly prepared data sets
If you don’t understand what’s in your data, it can lead to problems with the migration. Poor data can slow the migration and be problematic in the new environment.
If you move the wrong data in the migration, it can mean:- Fines that may incur from migrating sensitive data subject to regulations
- Transferring irrelevant data can lengthen the migration window, adding costs and delays
- Trying to correct the problem in the new environment, which takes time and resources away from other projects
- Improper methodology
Without awareness of the migration data set, you can’t pick the right migration tool. Choosing the wrong transfer method can overshoot budgets, underperform, or cause application downtime.
Using the wrong migration tool set can:- Slow the migration, running up costs and missing deadlines
- Cause data loss, if transfers aren’t able to sync with data as it changes
- Lead to delays and increase costs when tools that don’t work with the target repository are initially used
- Security issues
Permission and ACLs that existed in the original environment may not carry over into the new one. Fixing this problem manually can be a labor-intensive and time-consuming effort that will grind migration projects to a halt.
Overlooking security details in the data can cause a number of issues with a migration:- Accidentally granting global access may lead to data breaches
- Groups may need to be rebuilt in the new environment, which can be a time consuming process
- Access to some data may be revoked, causing delays
Data Migration Done Right
Since lack of insight into data is the major cause of migration failure, establishing such visibility is crucial to successfully transition to a new working environment. Proper data governance is the key to gaining that knowledge and using it effectively through every phase of the migration process.
NetApp has a way to solve the problems of improper data insights with BlueXP classification, powered by Cloud Data Sense. BlueXP classification automatically scans, maps, classifies, and reports your data in any type of storage repository.
For more on how NetApp can help, take a look at the next blog in this series where we dive into how BlueXP classification with Cloud Data Sense can meet all of the migration planning steps along the way, providing crucial data insights that will inform the right decisions to make your migration a success.

FAQ
- What happens if data migration fails?
Migration failures can lead to a number of different results. Most frequently, migrations fail in terms of the projected budgets and timelines, with companies spending more than expected and taking longer to get to the new environment. Both have tremendous business impacts.
But more technical failures also occur. Workloads may not operate properly in the new environment or require extensive effort to re-architect if not properly scoped. Security issues can follow when permissions break during the migration. Also, migrating the wrong data can both increase costs and lead to regulatory fines. - What are the main reasons for the cloud migration failures?
While there can be multiple reasons for cloud migration failures—improper project scoping, misaligned business goals, poorly prepared data sets, and security oversights—they all stem from one major cause: lack of insight into data.