Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
October 24, 2021
Topics: Cloud Volumes ONTAPCloud Manager AzureAdvanced3 minute read
In the previous blog, we covered how to mount file shares from NetApp® Cloud Volumes ONTAP to provide external storage to virtual machines (VMs) running on Azure VMware Solutions private cloud. Now, let’s look at configuring guest VMs to use software iSCSI and attach to the Cloud Volumes ONTAP software appliance. Because the guest must be specifically configured for iSCSI and connected to the appliance, I call this external storage. Many operating systems, Windows included, have free software iSCSI initiators available, so this is a common configuration. In this configuration, the ESXi host layer is not at all involved in any translation or management of the storage. The iSCSI traffic is simply another form of VM traffic that moves across the network interface cards (NICs).
Connect a LUN to the host
To connect a LUN to the host, complete the following steps:
- On the Canvas page, double-click the Cloud Volumes ONTAP working environment to create and manage volumes.
- Click Add Volume > New Volume, select iSCSI, and create the initiator group (igroup).
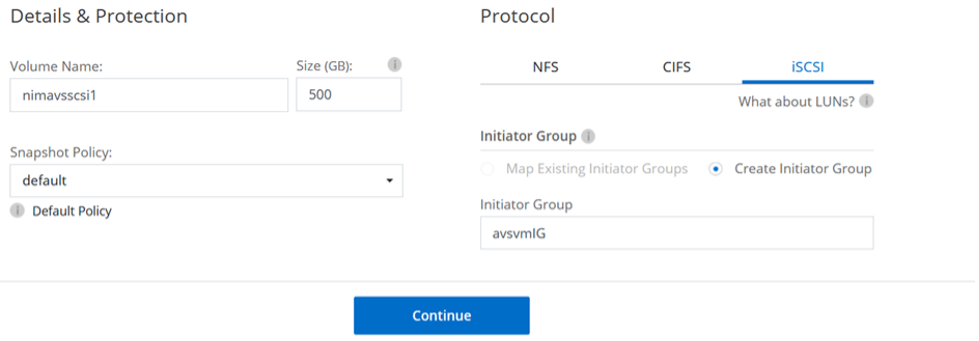
- After the volume is provisioned, select the volume, and then click Target IQN. Click Copy to copy the IQN name. Set up an iSCSI connection from the host to the LUN.
To accomplish the same:- RDP to the VM hosted on Azure VMware Solution software-defined data center (SDDC).
- Open the iSCSI Initiator Properties dialog box: Select Server Manager > Dashboard > Tools > iSCSI Initiator
- From the Discovery tab, click Discover Portal or Add Portal, and then enter the IP address of the iSCSI target port.
- From the Targets tab, select the target discovered, and then click Log on or Connect.
- Select Enable Multipath, select Automatically Restore This Connection When the Computer Starts or Add This Connection to the List of Favorite Targets, and then click Advanced.
Note: The Windows host must have an iSCSI connection to each node in the cluster. The native device-specific module (DSM) selects the best paths to use.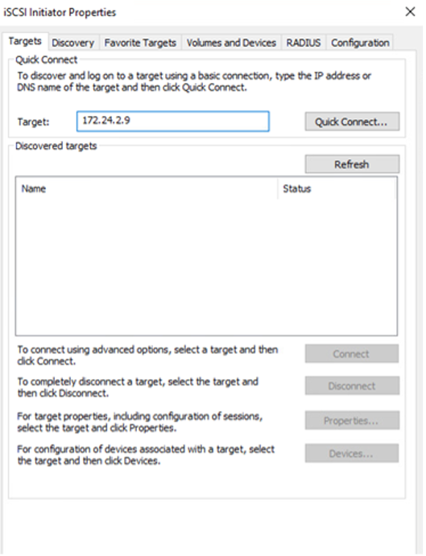
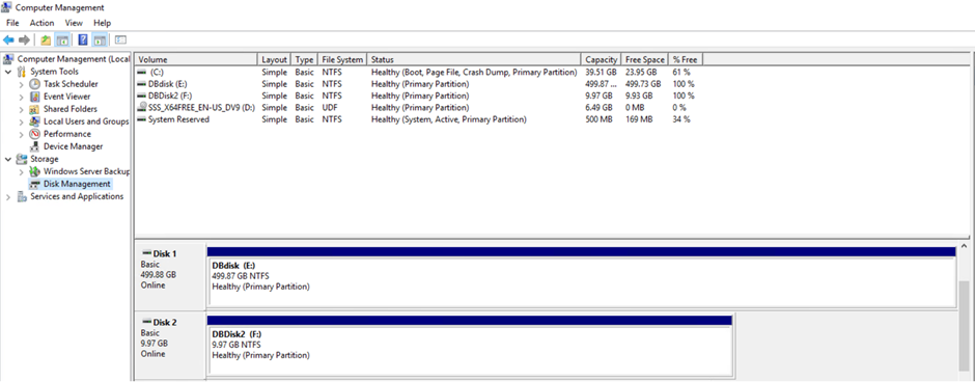
- LUNs on storage virtual machine (SVM) appear as disks to the Windows host. Any new disks added are not automatically discovered by the host. Trigger a manual rescan to discover the disks.
- Open the Windows Computer Management utility: Start > Administrative Tools > Computer Management.
- Expand the Storage node in the navigation tree.
- Click Disk Management.
- Click Action > Rescan Disks.
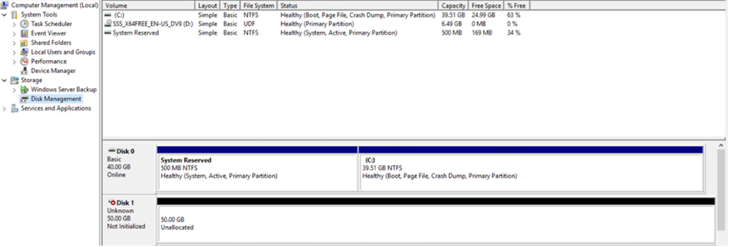
- When a new LUN is first accessed by the Windows host, it has no partition or file system. Initialize the LUN, and optionally format it with a file system:
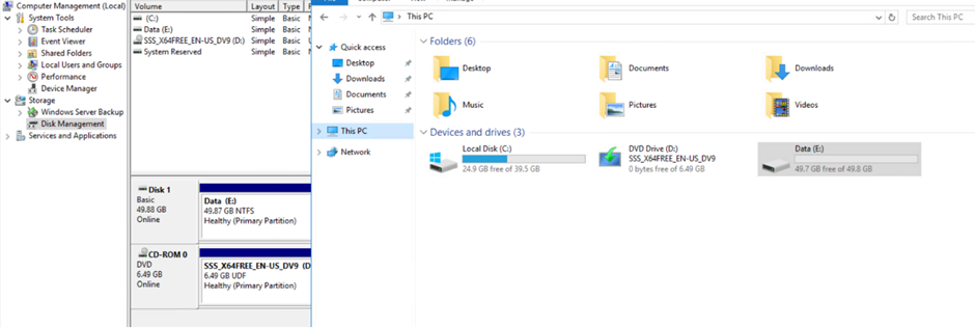
- Start Windows Disk Management.
- Right-click the LUN, and then select the required disk or partition type.
- Follow the instructions in the wizard. In this example, drive E is mounted.
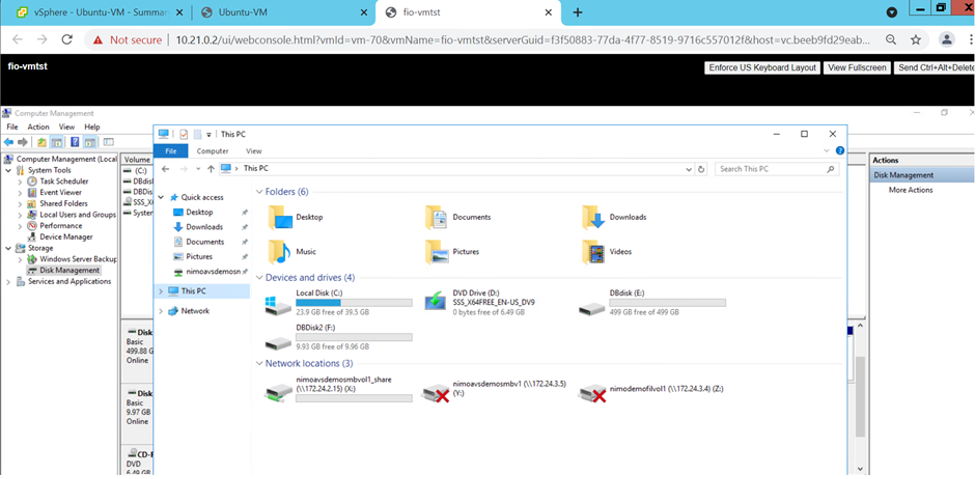
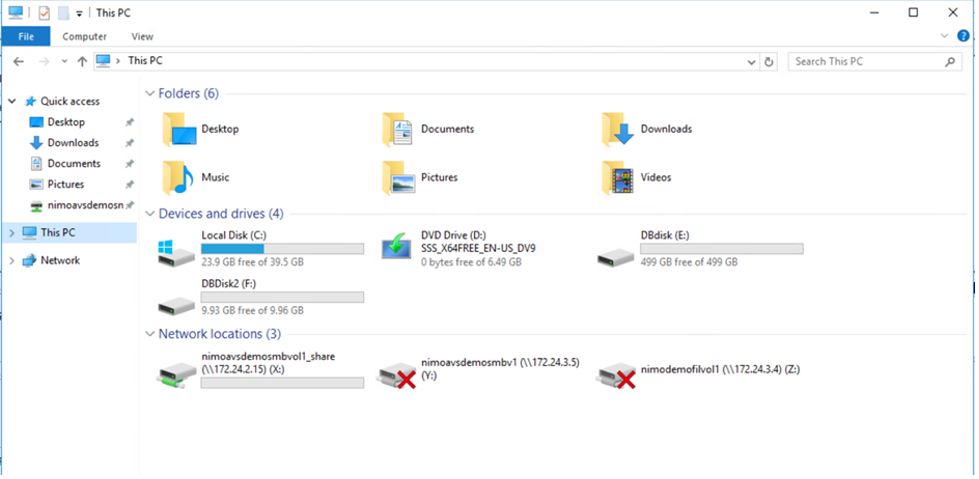
What’s Next?
So, what are you waiting for? Explore Azure NetApp Files and Cloud Volumes ONTAP and choose the appropriate option to offload the storage heavy workloads from vSAN to make your VMware deployment more cost effective. By combining the flexibility and performance of NetApp storage offerings with the native hybrid cloud capabilities of VMware Cloud, NetApp simplifies running all types of workloads without modifying applications and without compromising security or performance.