More about Compliance in the Cloud
- Azure Compliance Manager: A New Compliance Assessment Tool for Azure
- AWS Privacy Tools: Amazon Macie vs. NetApp Cloud Data Sense
- How to Configure Amazon Macie Master and Member Accounts
- What Is AWS Macie?: An Introduction to the Amazon S3 Data Reporting Tool
- AWS S3 Security: Getting More Secure Data Storage on Amazon S3
- Cloud Data Storage Architects:
How You Can Support Compliance
Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
August 17, 2020
Topics: Cloud Data Sense AWSAdvanced7 minute read
The data security requirements in the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR as it’s commonly known, have become a major consideration for enterprise IT teams both when designing their own systems and when selecting public cloud service providers and third-party systems.
With this new data privacy regulation and the ever-present risk of security breaches—such as when Facebook exposed more than 50 million users’ personal data—new services are being offered to help companies protect their users’ personal information. Personally identifiable information (PII) can be some of the most valuable and, at the same time, most sensitive business data that a company owns. This is especially relevant for cloud-based applications, where data is stored and managed on cloud servers, and secured using the cloud provider’s methodologies and protocols.
Data stored as such, requires an additional layer of defense. Understanding this challenge, AWS created AWS Macie to facilitate and improve data access monitoring, and supply instrumental information about unsecured data in the cloud.
What is AWS Macie? In this post we’ll take a look at AWS Macie, show you what this new service does, and how it can be enhanced by the compliance tools offered by NetApp Cloud Compliance for Amazon S3 buckets.
What Is AWS Macie?
Amazon Macie is a security monitoring tool that utilizes AWS’s AI engine for continuous analysis and content classification in Amazon S3 buckets. AWS Macie is able to learn the access patterns within the organization data and can visualize this access information, alert on anomalies and data security downgrades, and trigger compensatory actions in integrated SIEM tools.
But what is AWS Macie capable of? Currently, Macie supports monitoring and alerting on data stored in Amazon S3, but AWS plans to extend the tool’s coverage and abilities to Amazon EBS, Amazon S3 Glacier, and eventually to all the other data storage types it offers.
When activated, Macie starts scanning all the data in the S3 buckets that it is configured to monitor. The scan establishes a baseline of the data in the bucket, detailing who accesses it and with which protocols. From that point, every request to access this data is inspected and visualized on the Macie dashboard. Macie's behavior analytics engine identifies suspicious activity on the monitored data and has the ability to detect and notify on sudden increases in API activity, which might indicate an ongoing breach.
Using AWS’s ability to recognize the location from which requests are being sent, users can become aware of irregular API activity from multiple locations or at infrequent hours. Macie can also help to prevent future data loss by identifying patterns of access to data.
Via AWS CloudTrail, Macie has the ability to track errors related to content accessibility permissions and to designate a risk level between 1 and 10 for each CloudTrial error. Macie then executes automatic operations based on this risk level, such as alerting on controversial events or performing automatic configurations for the content managed in Amazon S3.
What Is AWS Macie Pricing?
Users can currently run Macie in one of two US regions—N. Virginia or Oregon—but the service has the same price in either region. AWS Macie pricing is composed of three components: the amount of content that Macie classifies, the number of AWS CloudTrail events that Macie assesses, and data retention. The basic package includes 30 days retention of generated metadata of classified S3 objects. Every month beyond this initial 30-day period has an extra cost per GB of metadata.
How DevOps And Storage Teams Use AWS Macie
How do DevOps and security teams gain the advantages of this AWS monitoring tool? The first thing to determine is which buckets contain the sensitive data and need to be monitored by AWS Macie. Since there isn’t an AWS service for determining which buckets contain sensitive data, users can turn to NetApp Cloud Compliance for Amazon S3 buckets.
Once a list of relevant S3 buckets is ready, the storage and DevOps team can start configuring Macie, the first step being—as with any AWS service—configuring IAM roles. AWS has several predefined policies for Macie, such as FullAccess and HandshakeRole, allowing account admins to give users the ability to configure Macie and its access to S3 buckets and to CloudTrail.
Once Macie’s roles are in place, and Macie has been given access to the AWS resources it requires, the storage team should configure the S3 buckets to be classified and monitored in the AWS Macie Integrations page, shown below.
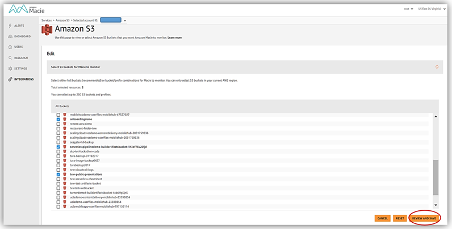 Figure 1: AWS Macie Integrations page - selecting S3 buckets (source: AWS blogs)
Figure 1: AWS Macie Integrations page - selecting S3 buckets (source: AWS blogs)
When the relevant S3 buckets are configured, Macie starts to scan the buckets and classify the data in them. Macie classifies and segments the data according to several categories and aspects, such as content type, file extension, theme, regex, and the different PII types, like full names and mailing and email addresses, billing information and birth dates. When the data is classified, Macie labels it with a respective risk level, and starts to monitor the usage of this data.
The data is monitored according to several metrics, and has a dashboard that contains a visualization for each of these metrics. The dashboard gives a clear view of the S3 objects lifecycle, showing how many objects are defined as critical, how many users access data in how many user sessions, and a classification graph based on the age of objects. The dashboard can also display the amount of S3 objects by PII, the amount of S3 objects and buckets that are publicly accessible and other graphs or lists of high risk objects or activity.
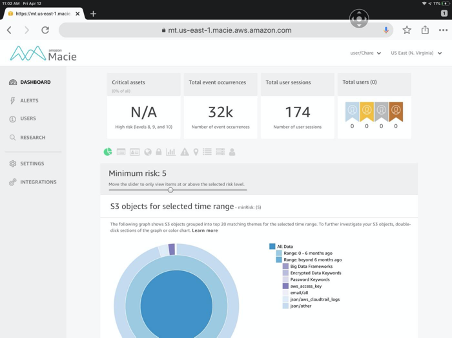 Figure 2: AWS Macie dashboard (source: Medium.com)
Figure 2: AWS Macie dashboard (source: Medium.com)
Macie allows deep dive into the data by building and running queries to single out and highlight the activity of specific S3 objects, according to the search criteria, which are very generic. Security engineers can run queries to filter and find objects accessed by a specific browser, in a specific time range. They can set a range of object size to be searched or look for content within the objects (for text or zipped files). Each of these queries can be saved and constantly executed with an alert configured for when the queries return new results.
Macie uses CloudWatch to dispatch AWS alerts to stakeholders and integrates with AWS Security Hub to send different third party systems a notification about the Macie alert. As Security Hub has integrations with many tools and systems, these notifications can be utilized to automate processes for improved security and better collaboration on these incidents.
What Is AWS Macie? A Final Assessment
AWS Macie is a machine-learning based classification tool for content stored in S3 buckets. It identifies and monitors sensitive and risky information which, if inappropriately exposed, may lead to devastating consequences. It solves many data management challenges by evaluating the security risk of every object and alert on possible unauthorized usage of the object.
But what storage and DevOps teams always remember and security engineers must learn is that misconfigured Macie coverage and alert rules might create a lot of false positive alerts and lead to losing trust in the tool and it’s abilities. Being a monitoring tool, it must be constantly reviewed and optimized so it will satisfy the compliance and security requirements cloud based organizations have.
There is a concern when it comes to pinpointing the sensitive data stored in an unstructured format in your buckets. If you don’t know where to find the sensitive data in use, how will you know where to run AWS Macie? Since a component of AWS Macie pricing includes the amount of data classified, simply running the service on all your data may be a cost concern. For users who are looking for an automated way to pinpoint where their data is stored and to report on it instantly, Cloud Compliance for Amazon S3 buckets offers a viable alternative.
This data mapping tool for Amazon S3 buckets uses an AI-driven algorithm to parse personal data, determining which information needs to be flagged and which can be ignored, so only the relevant data in S3 buckets can be focused on. It is also available for use with NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP and NetApp Azure Files.
Private data is about more than PII. Try Cloud Compliance for Amazon S3 buckets today.
