Subscribe to our blog
Thanks for subscribing to the blog.
What is Azure Files Backup?
Azure Files Backup provides cloud-based backup for data stored in Azure Files shares. The solution is designed to work natively with Azure Backup, which is the main backup service offered by Azure. To set this up, you need to integrate Azure File Sync with Azure Backup, and then you can securely centralize all your file share data and any backups you create. Once you set this up, you can configure backup and disaster recovery measures to ensure the protection of your data during disasters.
In this article, you will learn:
- Key Benefits of Azure File Share Backup
- What are Azure Files Snapshots?
- How Azure Files Backup Works Behind the Scenes
- Quick Start Guide: How to Configure Azure Files Backup
- Optimized Azure File Storage with Cloud Volumes ONTAP and Azure NetApp Files
- Azure Files Backup Q&A
Key Benefits of Azure File Share Backup
- Simple and integrated: Azure File Share Backup is natively integrated with Azure Files, which makes it easy to configure and manage backups for your file shares without the need for additional infrastructure or software.
- Centralized management: Azure Backup provides a centralized interface for managing and monitoring backups across all your Azure resources, including file shares, virtual machines, and databases.
- Incremental backups: Azure File Share Backup supports incremental backups, meaning that only the changes made since the last backup are transferred. This reduces storage and bandwidth consumption, making the backup process more efficient.
- Data retention: You can define custom data retention policies to meet your organization's requirements, allowing you to retain backups for as long as necessary.
- Granular recovery: Azure File Share Backup allows you to restore individual files or entire file shares as needed, giving you granular control over the recovery process.
- Backup consistency: Azure File Share Backup supports both crash-consistent and application-consistent backups, ensuring that your data is recoverable in a consistent state.
- Monitoring and alerts: Azure Backup provides monitoring and alerting capabilities, enabling you to track the progress of your backups and receive notifications of any issues that may arise.
- Cost-effective: Azure File Share Backup is a cost-effective solution, as you only pay for the storage used by your backups. Incremental backups further help in reducing storage costs.
What are Azure Files Snapshots?
Azure Files lets you create point-in-time snapshots of file shares. You can use snapshots to recover data after accidental deletion, unwanted changes, or data corruption. Another use is for periodic backups of a file share, for disaster recovery purposes or to meet your auditing or compliance obligations.
Azure Files snapshots provide the following capabilities:
- Create, delete, copy, and manage snapshots via Azure Portal, CLI, or REST API
- Snapshots of a share are accessible via SMB protocol, similar to a live share—you can retrieve a file share’s contents and mount it as a drive
- Retrieve data from file share snapshots at the individual file level, allowing users to retrieve specific files they lost or deleted
- Retain snapshots for as long as required—until explicitly deleted or until the base file share is deleted
- Easily track snapshots associated with a base file share
Take into account following snapshot limitations:
- Snapshots cannot be modified after they are created
- The snapshot copy operation does support copying a snapshot to another Azure storage account—you can do this manually using a file copy utility like AzCopy
- You can have up to 200 snapshots per storage account
- Snapshots can only protect file shares at the file level—for example, they cannot help recover from accidental deletion of an entire storage account. To protect against broader deletion scenarios, enable soft delete or lock the storage account.
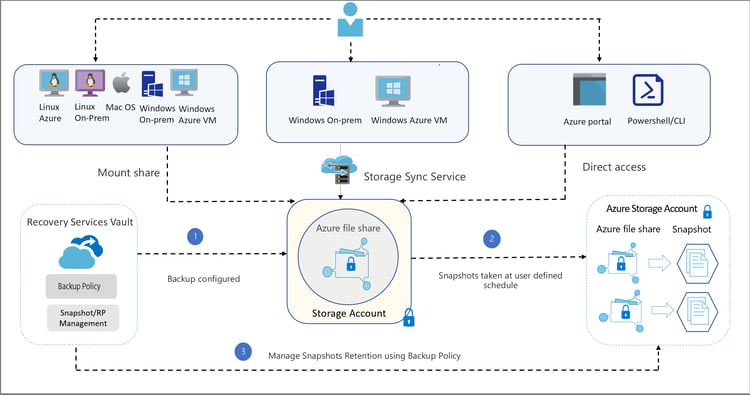
How Azure Files Backup Works Behind the Scenes
 Source: Azure
Source: Azure
Here are some architecture processes that work behind the scenes once backup is enabled:
- Azure Backup creates file share snapshots using the File Share API. The system stores only the snapshot URL in the metadata pool.
- The system lets you restore Azure file share contents from snapshots available on a source file share. You can either restore individual files or the entire share. Once this operation is triggered, the system retrieves the snapshot URL from the metadata pool. The data is then listed and shifted from a source snapshot to a target file share.
- When using Azure File Sync with Azure Backup, the backup service determines the paths of restored files. This path triggers a background change detection process that runs on the files. All changed files are then synced to the server endpoint.
- All backup and restore monitoring data is pushed into Azure Backup Monitoring. This process lets you monitor file share backups in one dashboard. Additionally, the monitoring service lets you set up your own alerts and email notifications for certain metrics that can let you know when backup health is affected.
Quick Start Guide: How to Configure Azure Files Backup
Here are a few steps to guide you through the initial configuration:
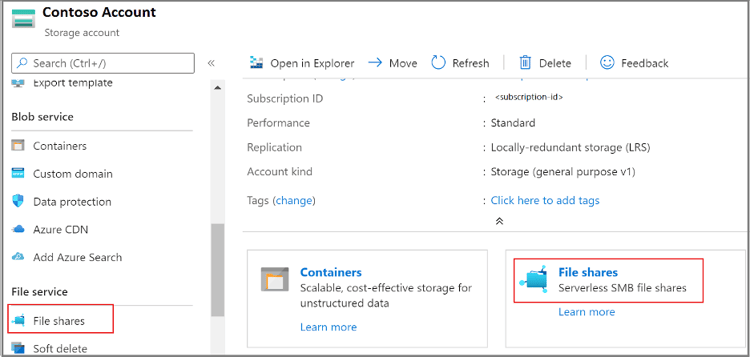
1. Go to the Azure portal—log into your account.
2. Create a Recovery Services vault—provides you with a storage entity you can use to view all of your backups across several workloads.
3. Choose a storage account—after creating the vault, Azure Backup looks for all storage repositories in your account. Choose the storage account containing your file shares. Once you choose an account, Azure Backup displays the sets of file shares in your account and stores their names in a management-layer catalog
4. Configure a backup policy—schedules and retains backups based on your requirements.
5. Select the file shares—you want to back up. Azure Backup service will then register the schedules you have set up into the control plane.
 Source: Azure
Source: Azure
After you set up the policy and enable it, the Azure Backup scheduler starts triggering backups according to the pre-configured timeframes.
Optimized Azure File Storage with Cloud Volumes ONTAP and Azure NetApp Files
NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP, the leading enterprise-grade storage management solution, delivers secure, proven storage management services on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Cloud Volumes ONTAP capacity can scale into the petabytes, and it supports various use cases such as file services, databases, DevOps, or any other enterprise workload, with a strong set of features including high availability, data protection, storage efficiencies, Kubernetes integration, and more.
In particular, Cloud Volumes ONTAP provides centralized file storage management, serving NAS, including NFS, SMB / CIFS as well as iSCSI and S3, and multiprotocol access.
Learn more about how Cloud Volumes ONTAP helps to address the challenges of file sharing in these Cloud Volumes ONTAP Customer Case Studies.
Azure NetApp Files is another file storage managed service alternative from Microsoft Azure built on NetApp technology, giving you enterprise file share capabilities that can support even your core business applications.
Azure Files Backup Q&A
What is Azure Backup?
Azure Backup lets you create isolated and independent backups. You can use these backups to protect your data against accidental destruction. Azure stores your backups in Recovery Services vaults that come with a built-in management of recovery points. Azure Backup is relatively simple to configure and scale. The system optimizes backups, and lets you easily restore backups as needed.
What Determines the Overall Cost of Azure Backup?
Azure Backup is offered at fixed prices, calculated according to the number of protected instances. In addition to these costs, there are other factors that impact the overall cost. Storage and bandwidth costs for your backups are charged separately from the fixed instance pricing. When planning your backup strategy, remember to choose the storage space and bandwidth that suits your budget.
What is Azure File Storage?
Azure File Storage lets you access and store data in file formats that work both in the cloud and on-premises. You can set up access to Azure Files shares using the SMB protocol or a REST API. You can also use the Azure File Sync service. Once you set up this integration, you can share files between the Azure cloud and on-premise Windows Server instances.
